bart poisson#
=================================================================================================================
The bart poisson command in the BART is used to construct a binary Poisson-disk sampling mask. This type of mask is useful for undersampling k-space data in MRI, which can accelerate the scan.
Purpose: It generates a binary mask that can be applied to k-space data to simulate undersampling.
Poisson-Disk Sampling: is a technique for randomly picking tightly-packed points but with a minimum distance constraint between them.
Where we can view the full usage string and optional arguments with the -h flag.
!bart poisson -h
Usage: poisson [-Y d] [-Z d] [-y f] [-z f] [-C d] [-v] [-e] [-s d] <output>
Computes Poisson-disc sampling pattern.
-Y size size dimension 1
-Z size size dimension 2
-y acc acceleration dim 1
-z acc acceleration dim 2
-C size size of calibration region
-v variable density
-e elliptical scanning
-s seed random seed
-h help
Examples (python)#
# Importing the required libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import cfl
from bart import bart
Exmaple 1#
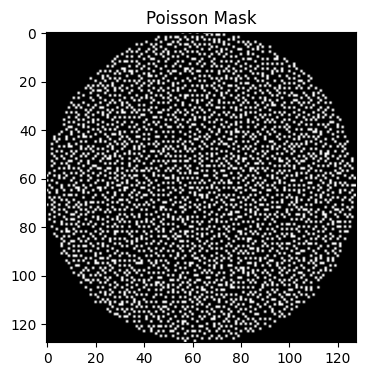
-Y 128: Specifies a 128-point size for the first dimension.
-y 10: Specifies an acceleration factor of 10 along this dimension.
poisson_mask_1 = bart(1, 'poisson -Y 128 -y 10').squeeze()
points: 1624, grid size: 128x128 = 16384 (R = 10.088670)
# Visualizing the images using Matplotlib
plt.figure(figsize=(4,6))
plt.imshow(abs(poisson_mask_1), cmap='gray')
plt.title('Poisson Mask')
plt.show()
Exmaple 2#
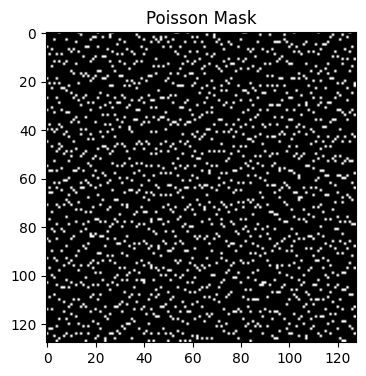
-Y 128: Sets the size of dimension 1 (128).
-Z 128: Sets the size of dimension 2 (128).
-y 10: Acceleration factor 10× along dimension 1.
-z 5: Acceleration factor 5× along dimension 2.
poisson_mask_2 = bart(1, 'poisson -Y 128 -Z 128 -y 10 -z 5').squeeze()
points: 327, grid size: 128x128 = 16384 (R = 50.103977)
# Visualizing the images using Matplotlib
plt.figure(figsize=(4,6))
plt.imshow(abs(poisson_mask_2), cmap='gray')
plt.title('Poisson Mask')
plt.show()
Exmaple 3#
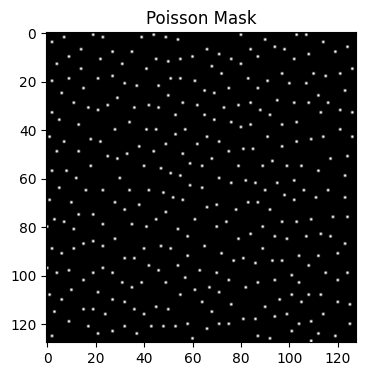
-Y 128: Sets the first dimension size to 128.
-Z 128: Sets the second dimension size to 128.
-y 2: Acceleration factor 2× along dimension 1.
-z 2: Acceleration factor 2× along dimension 2.
-v: Enables variable-density Poisson-disc sampling, leading to denser sampling in the center and sparser sampling in outer regions.
poisson_mask_3 = bart(1, 'poisson -Y 128 -Z 128 -y 2 -z 2 -v').squeeze()
points: 1557, grid size: 128x128 = 16384 (R = 10.522800)
# Visualizing the images using Matplotlib
plt.figure(figsize=(4,6))
plt.imshow(abs(poisson_mask_3), cmap='gray')
plt.title('Poisson Mask')
plt.show()
Exmaple 4#
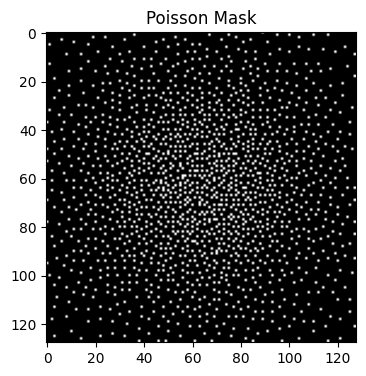
-e: Enables elliptical scanning, meaning the sampling follows an elliptical shape rather than a full rectangular grid.
poisson_mask_4 = bart(1, 'poisson -Y 128 -Z 128 -y 2 -z 2 -e').squeeze()
points: 3207, grid size: 128x128x(pi/4) = 12867 (R = 4.012462)
# Visualizing the images using Matplotlib
plt.figure(figsize=(4,6))
plt.imshow(abs(poisson_mask_4), cmap='gray')
plt.title('Poisson Mask')
plt.show()